Industry 4.0: Exploring the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Blog
4 Min Read
In the past few decades, we have witnessed a series of technological advancements that have transformed the way we live, work and communicate. From the internet to smartphones, from social media to cloud computing, these technological innovations have revolutionized every aspect of our lives. However, one sector that has seen a particularly significant impact of these advancements is the manufacturing industry. With the emergence of Industry 4.0, we are witnessing a new wave of technological transformation that is set to revolutionize the way we produce goods and services.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is the integration of advanced technologies into the manufacturing process to create a highly automated, efficient, and interconnected system. The term Industry 4.0 was first coined in 2011 by the German government to describe their vision of the future of manufacturing. The concept of Industry 4.0 builds upon the three previous industrial revolutions, which were characterized by the following innovations:
The Evolution of Industry 4.0
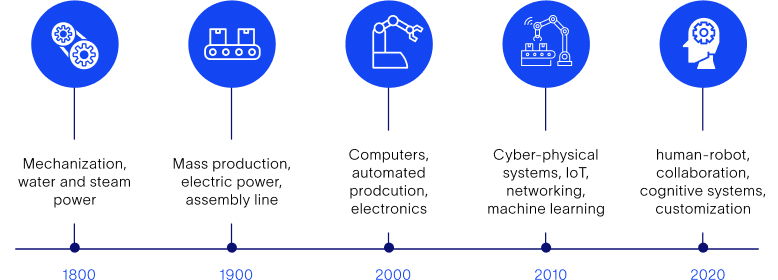
- The First Industrial Revolution (1760-1840)
The First Industrial Revolution (1760-1840) marked a significant shift in the manufacturing industry, with the introduction of mechanization through the use of water and steam power. Prior to this period, goods were largely produced by hand, in small batches, and by skilled artisans. However, with the development of the steam engine and the widespread use of water power, the manufacturing industry began to transition to larger, more centralized factories.One of the most notable developments of the First Industrial Revolution was the mechanization of the textile industry. Prior to this period, the production of textiles was largely done by hand, with each stage of the process being carried out by individual artisans. However, with the introduction of textile machinery such as the spinning jenny, the power loom, and the cotton gin, the textile industry was able to produce textiles on a much larger scale and at a much faster rate.
- The Second Industrial Revolution (1870-1914)
The Second Industrial Revolution (1870-1914) was marked by the introduction of mass production through the use of electricity and the assembly line. This period saw the growth of industries such as the automotive and electronics industries, which were able to produce goods on an unprecedented scale and at a much lower cost. One of the key developments of the Second Industrial Revolution was the introduction of electricity as a source of power. This allowed factories to operate more efficiently and at a lower cost than ever before, as machines could be powered by electricity rather than steam or water. Electricity also allowed for greater flexibility in production, as machines could be turned on and off as needed, rather than running continuously. - Process Integration
Process integration involves connecting different business processes and workflows across various systems to create a unified and streamlined process. This type of integration helps organizations to reduce errors, increase efficiency, and improve overall business performance. For example, a legacy system might have a separate process for inventory management, while a newer system might handle order processing. By integrating these systems at the process level, businesses can automate the flow of data between them, allowing for real-time visibility into inventory levels and order processing. This integration can also help businesses optimize their supply chain management, reduce lead times, and improve customer satisfaction. - The Third Industrial Revolution (1969-2000)
The Third Industrial Revolution (1969-2000) was marked by the introduction of computerization and automation, which had a profound impact on the manufacturing industry. This period saw the development of technologies such as computers, robotics, and automation, which revolutionized the way goods were produced and manufactured.
One of the key developments of the Third Industrial Revolution was the introduction of computerization. This allowed for greater precision and accuracy in production, as computers could control machines with a high degree of accuracy. This led to significant increases in productivity and efficiency, as goods could be produced with a much higher level of consistency and quality.
Industry 4.0 takes the automation and connectivity of the third industrial revolution to a whole new level by combining advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and cloud computing.
Key Technologies of Industry 4.0
The following are the key technologies that are driving the Industry 4.0 revolution:
- The Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity to exchange data with other devices and systems. In the context of Industry 4.0, Industrial Internet of Things- IIoT enables the interconnection of machines and devices in the manufacturing process, enabling real-time data sharing and analytics. - Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, and decision-making. In the context of Industry 4.0, Manufacturing Intellegence (MI) is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. - Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics refers to the process of analyzing large and complex data sets to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights. In the context of Industry 4.0, big data analytics is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. - Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. In the context of Industry 4.0, cloud computing is used for data storage, data sharing, and real-time analytics.
Why Industry 4.0 is Important
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, has several benefits for businesses and society as a whole. Here are some of the key benefits of Industry 4.0:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) can help businesses optimize their operations, reduce waste, and increase efficiency. This leads to higher productivity, lower costs, and better quality products. - Customization and personalization
Industry 4.0 technologies allow businesses to offer customized and personalized products and services to their customers. With the help of digital technologies such as 3D printing and digital twins, businesses can create unique products tailored to individual customers’ needs and preferences. - Better decision-making
Industry 4.0 technologies provide businesses with real-time data and analytics, enabling them to make better decisions. This helps businesses identify and solve problems quickly, improve processes, and respond to changing market conditions. - Improved safety
Industry 4.0 technologies such as robotics and automation can help reduce the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. By automating hazardous tasks, businesses can create a safer work environment for their employees. - New business models and revenue streams
Industry 4.0 technologies can enable businesses to create new revenue streams and business models. For example, businesses can use IoT sensors to collect data on how their products are used and offer new services based on this data. - Sustainable practices
Industry 4.0 technologies can help businesses reduce their environmental impact. For example, by using predictive maintenance to reduce equipment downtime, businesses can reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Industry 4.0 technologies are designed to improve business operations by incorporating digital technologies into the physical world. These technologies have the potential to transform the way businesses operate and create value in several ways.
One of the key benefits of Industry 4.0 technologies is improved efficiency. By automating manual processes and optimizing operations, businesses can significantly reduce the time and effort required to complete tasks. This not only improves productivity, but it also reduces costs, allowing businesses to allocate resources more effectively.
Our INDUSTRY 4.0 Services
INS3 services are designed to help manufacturers fully embrace the Industry 4.0 digital revolution and transform their operations into more efficient, productive, and sustainable systems. We provide a range of services that enable companies to implement cutting-edge technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Big Data Analytics, Manufacturing Intelligence, and Data Infrastructure. Our team of experts works closely with clients to understand their unique needs and challenges, and then develop customized solutions that align with their strategic goals. Our focus is on driving measurable results and delivering value to our clients through improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced customer experiences, and increased competitiveness. With our Industry 4.0 services, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities, accelerate growth, and stay ahead of the curve in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Our Industry 4.0 Workshop
Our Industry 4.0 workshop is a comprehensive learning experience designed to equip participants with the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed in the rapidly-evolving landscape of the fourth industrial revolution. Throughout the workshop, participants will gain an understanding of the technologies, trends, and business models that are shaping Industry 4.0, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Manufacturing Intelligence (MI), and Cloud Computing. They will also learn how to identify opportunities for innovation and growth in their own organizations, and develop strategies for implementing Industry 4.0 solutions. Through a combination of lectures, case studies, and hands-on exercises, our Industry 4.0 workshop provides a dynamic and engaging learning environment that will leave participants feeling confident and prepared to navigate the exciting new world of Industry 4.0.
Download INS3 Guide for Digital Transformation
Schedule a walk-through with INS3 to assess your needs and evaluate the appropriate path for your digital transformation journey
Download INS3 Guide for Digital Transformation
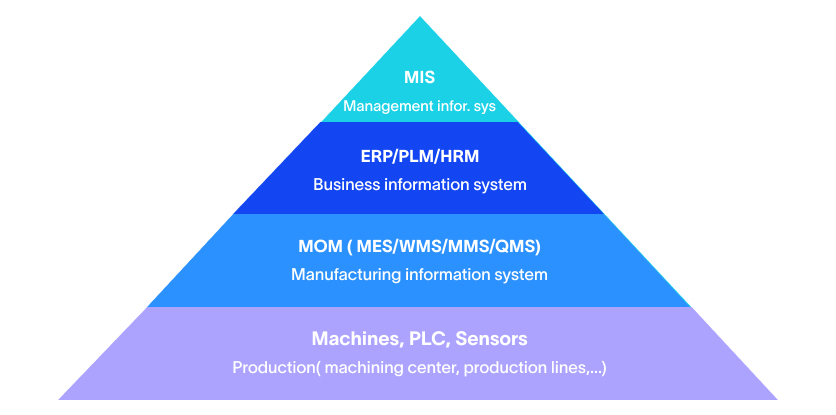
Agile MES: The Key to Unlocking Smart Manufacturing Success
MES is a computerized system used in manufacturing operations to track and document the transformation of raw materials into finished goods. An MES system typically manages and monitors work orders, equipment, materials, and personnel on the shop floor. The system provides real-time visibility into production processes, helps optimize manufacturing operations, and improves the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
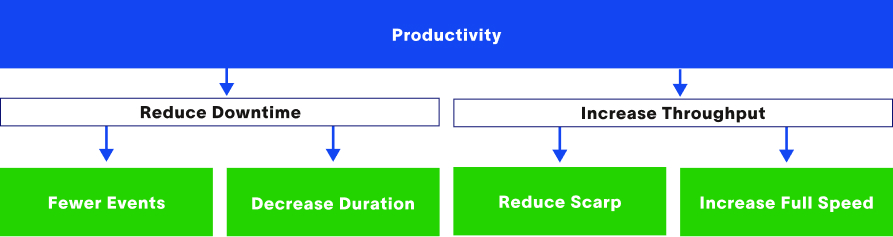
Understanding OEE: The Key to Manufacturing Efficiency
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, improving efficiency and productivity is crucial for businesses to remain competitive. One of the key metrics used to measure manufacturing efficiency is OEE or Overall Equipment Effectiveness. In this blog, we will take a closer look at OEE and its importance in manufacturing.
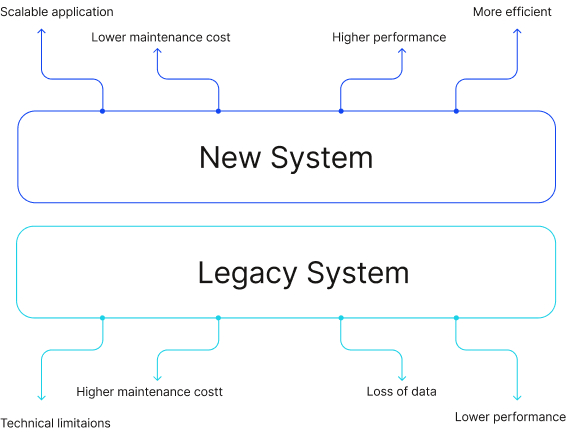
How to Effectively Conduct a Legacy System Integration
Legacy system integration can be a daunting task, but it’s a necessary one for many manufacturers that rely on outdated systems to run their business. Integrating legacy systems with modern technology can improve efficiency, streamline processes, and save time and money. However, it’s important to approach the integration process carefully and methodically to ensure success.
Share on :
Keep On Reading
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters to get updates regarding our new production, behind the scene process of our art creation and much more.
After submitting this form you will receive an e-mail with a confirmation link that you must click to complete your request. Detailed information on processing and cancellation can be found in our privacy policy.


