Maximizing Industrial Efficiency: The Power of SCADA System Integration
Blog
4 Min Read
Introduction to SCADA Systems
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. SCADA systems are used in various industries, including Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals & Life Sciences, Chemical and Industrial, Water / Wastewater, Manufacturing and Discrete, and Energy & Power.
These systems allow operators to monitor and control industrial processes remotely, collect data, and analyze trends.
SCADA systems consist of three main components
- The remote terminal unit (RTU): The RTU is responsible for collecting data from sensors and equipment, processing it, and sending it to the supervisory computer system.
- The supervisory computer system: The supervisory computer system collects and stores data from multiple RTUs and provides a user interface for operators to view and manage industrial processes.
- The human-machine interface (HMI): The HMI is the graphical user interface that operators use to interact with the supervisory computer system.
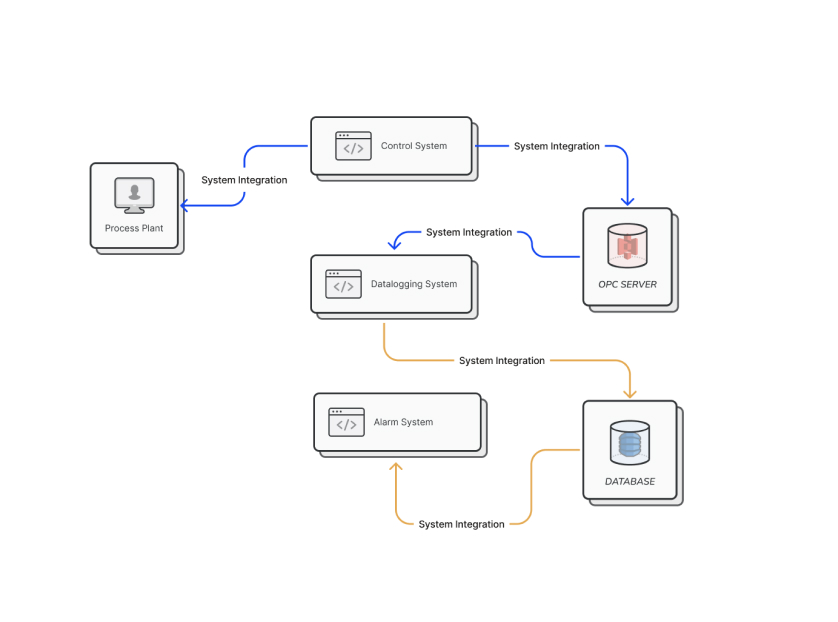
SCADA System Integration
SCADA system integration involves connecting SCADA systems to other systems within an organization or across multiple organizations. This integration allows data to be shared and analyzed across systems, leading to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and better decision-making.
The integration of SCADA systems can be done in various ways, including:
- Protocol Integration
Protocol integration is an essential aspect of SCADA system integration. SCADA systems use various communication protocols to exchange data with other systems, and different systems may use different protocols, which can make it challenging to exchange data between them.
Protocol integration involves converting data between different protocols to enable data exchange between SCADA systems and other systems. The process of protocol integration starts with identifying the protocols used by each system and the data that needs to be exchanged. Once the protocols are identified, a protocol conversion device or software can be used to convert the data between the protocols. - Database Integration
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used in many industries to monitor and control various processes, such as manufacturing, energy production, and water treatment. These systems often store data in their own databases, which can include real-time process data, historical data, and alarm logs.
Database integration involves integrating these SCADA system databases with other databases within an organization or across multiple organizations. - Application Programming Interface (API) Integration
API integration is a method that enables SCADA systems to exchange data with other software applications through the use of APIs. Many SCADA systems come equipped with APIs that facilitate data exchange with other systems.
This allows for seamless data integration, making it easier to share data and communicate between different software applications. By utilizing the SCADA system’s API, data can be exchanged efficiently and effectively between different systems, enabling better coordination and decision-making. - Web Services Integration
Web services integration involves the use of web services to facilitate data exchange between systems. Web services are a standardized way of exchanging data between different applications, regardless of their programming language, platform, or location. They are typically based on the XML (eXtensible Markup Language) format and operate over the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) protocol.
In the context of SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, web services integration can be used to exchange data between different SCADA systems, or between SCADA systems and other systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) systems. This can help to improve the efficiency of data transfer and reduce the risk of errors or inconsistencies.
Benefits of SCADA System Integration
SCADA system integration offers several benefits, including:
Benefit 01
Improved Efficiency
SCADA system integration allows data to be shared and analyzed across systems, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
When different SCADA systems are integrated, data can be shared and analyzed across systems in real-time. This can help operators make more informed decisions and identify potential issues before they become major problems. For example, if a component in one system is not functioning properly, data from other systems can be used to identify the cause of the issue and take corrective action.
SCADA system integration can also improve efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing manual intervention. For example, if data from one system can be automatically fed into another system, operators don’t have to spend time manually entering the same data into multiple systems. This can help reduce errors and save time.
Benefit 02
Better Decision-making
SCADA system integration provides operators with access to real-time data from multiple systems, allowing them to make better-informed decisions.
When SCADA systems are integrated, data from multiple sources can be combined and analyzed in real-time. This can provide operators with a more complete picture of what’s happening in the production process, allowing them to identify potential issues and take corrective action before they become major problems.
For example, if data from a temperature sensor in one system indicates that a component is overheating, data from other systems can be used to identify the cause of the issue and take corrective action. Similarly, if data from a pressure sensor in one system indicates that a pipeline is under stress, data from other systems can be used to identify the source of the stress and take corrective action.
Benefit 03
Cost Savings
SCADA system integration reduces the need for manual data entry and increases data accuracy, leading to cost savings.
Manual data entry can be time-consuming and prone to errors, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. When SCADA systems are integrated, data can be automatically transferred between systems, reducing the need for manual data entry. This can help reduce errors and save time, which can lead to cost savings.
In addition, integration can help improve data accuracy. When data is automatically transferred between systems, the risk of errors introduced during manual data entry is reduced.
This can help improve the accuracy of data, which can help improve decision-making and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Benefit 04
Identify integration requirements
SCADA system integration allows for better security monitoring and control, leading to improved security.
When SCADA systems are integrated, it is easier to monitor and control security across multiple systems.
This can be particularly important in critical infrastructure environments, where the consequences of a security breach can be severe.
SCADA systems play a crucial role in many industries by allowing operators to monitor and control industrial processes remotely. SCADA system integration offers several benefits, including improved efficiency, better decision-making, cost savings, and improved security. There are various ways to integrate SCADA systems with other systems, including protocol integration, database integration, API integration, and web services integration. Organizations that integrate their SCADA systems with other systems can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and overall operational performance.
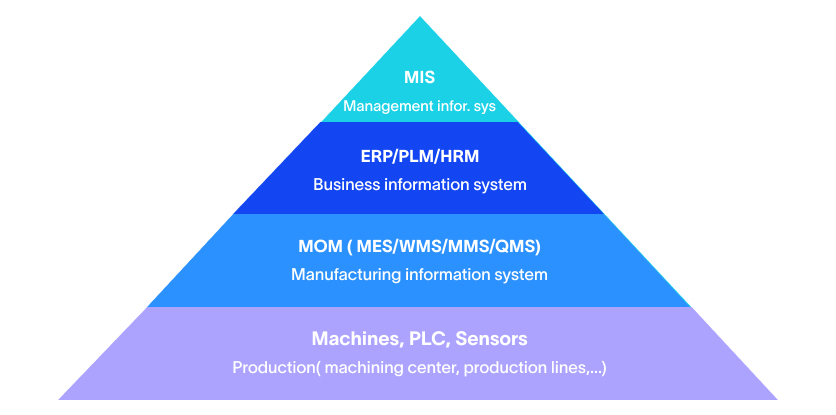
Agile MES: The Key to Unlocking Smart Manufacturing Success
MES is a computerized system used in manufacturing operations to track and document the transformation of raw materials into finished goods. An MES system typically manages and monitors work orders, equipment, materials, and personnel on the shop floor. The system provides real-time visibility into production processes, helps optimize manufacturing operations, and improves the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Understanding OEE: The Key to Manufacturing Efficiency
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, improving efficiency and productivity is crucial for businesses to remain competitive. One of the key metrics used to measure manufacturing efficiency is OEE or Overall Equipment Effectiveness. In this blog, we will take a closer look at OEE and its importance in manufacturing.
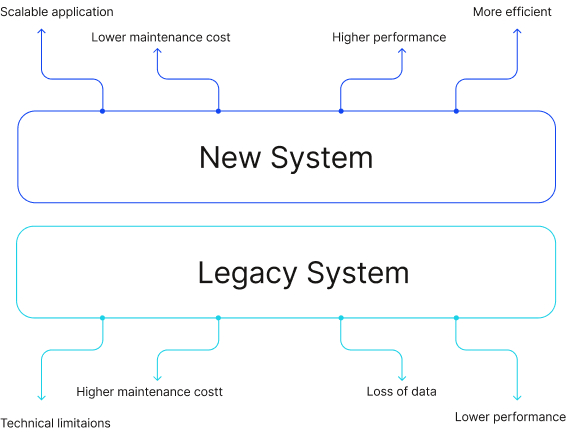
How to Effectively Conduct a Legacy System Integration
Legacy system integration can be a daunting task, but it’s a necessary one for many manufacturers that rely on outdated systems to run their business. Integrating legacy systems with modern technology can improve efficiency, streamline processes, and save time and money. However, it’s important to approach the integration process carefully and methodically to ensure success.
Share on :
Keep On Reading
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters to get updates regarding our new production, behind the scene process of our art creation and much more.
After submitting this form you will receive an e-mail with a confirmation link that you must click to complete your request. Detailed information on processing and cancellation can be found in our privacy policy.


